About Radiofrequency ablation
Radiofrequency ablation is minimally invasive, target selective technique that has been in clinical use for more than 3 decades and it is effective in chronic pain condition. Radiofrequency is a neurolytic technique that uses heat to produce controlled tissue ablation (thermocoagulation) and thus reduce pain by modulation pain transmission, without causing clinical sign of nerve damage. Pain relief can be last for many years and procedure can be repeated. It involves the use of a special equipment to produce high frequency energy of 300 to 500 kHz similar to one use in radio-transmitter, and the current termed RF current. Successful use of these technique requires specialized training and in-depth knowledge of neural anatomy.
Principles of Physics & Lesion
A high frequency current 500 kHz produced by RF generator machine apply on neural tissue through a closed circuit produce neurolysis of target nerve. With the use of this specialized generator, heat energy is created and delivered with precision to target nerves that carry pain impulses. The resulting “lesion” involves a spherical area of tissue destruction at the tip of the RF needle that can include pain-carrying nerves.
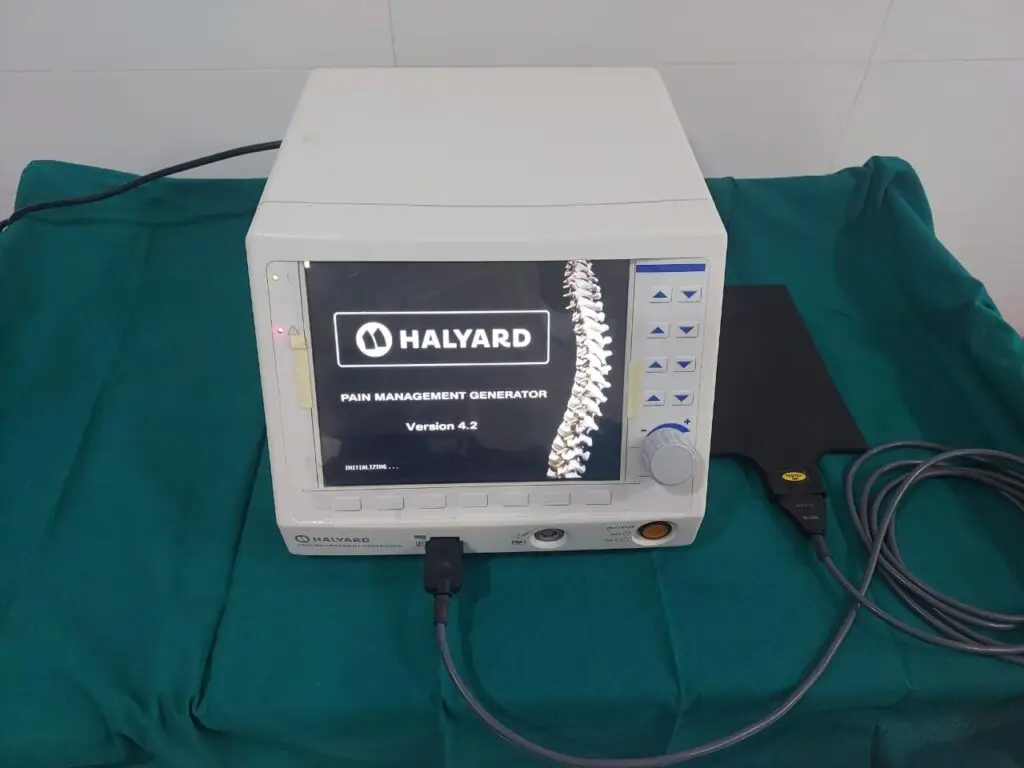

RF generator machine – multi channel (Halyard Avanos USA)
Size of lesion is determined by following factors
- Electrode tip size
- Temperature
- Time
- Rate of Thermal equilibrium
- Local tissue characteristics
TYPES OF RADIOFREQUENCIES
-
Conventional Radiofrequency
In this we uses temperature range from 45’ C to 90’ C to ablate the only sensory nerve for permanent block. -
Pulsed Radiofrequency
This is called neuromodulation in which we uses 42’ C temperature so it is not going to damage the nerve. It is helpful for ablation of sensory and motor combined nerve.
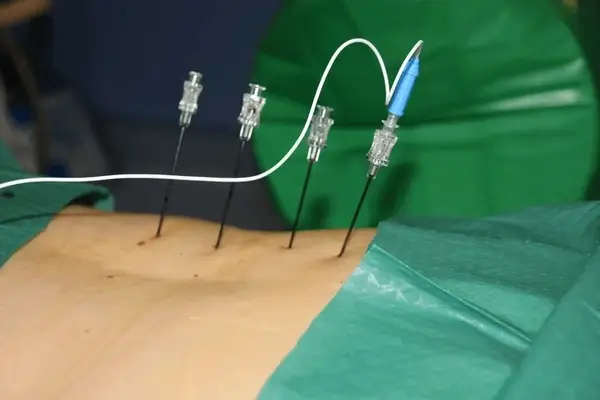
PROCEDURE OF RFA
Radiofrequency current deliver by 27 G thermocouple probe. That probe is inserted in long insulated cannula with different length and different lesion size bare area.
This procedure we do under IITV, USG or CT SCAN guidance with all aseptic and antiseptic precaution in operation theatre.
Before doing RF usually we check for sensory and motor nerve stimulation, to prevent unintentional nerve damage.
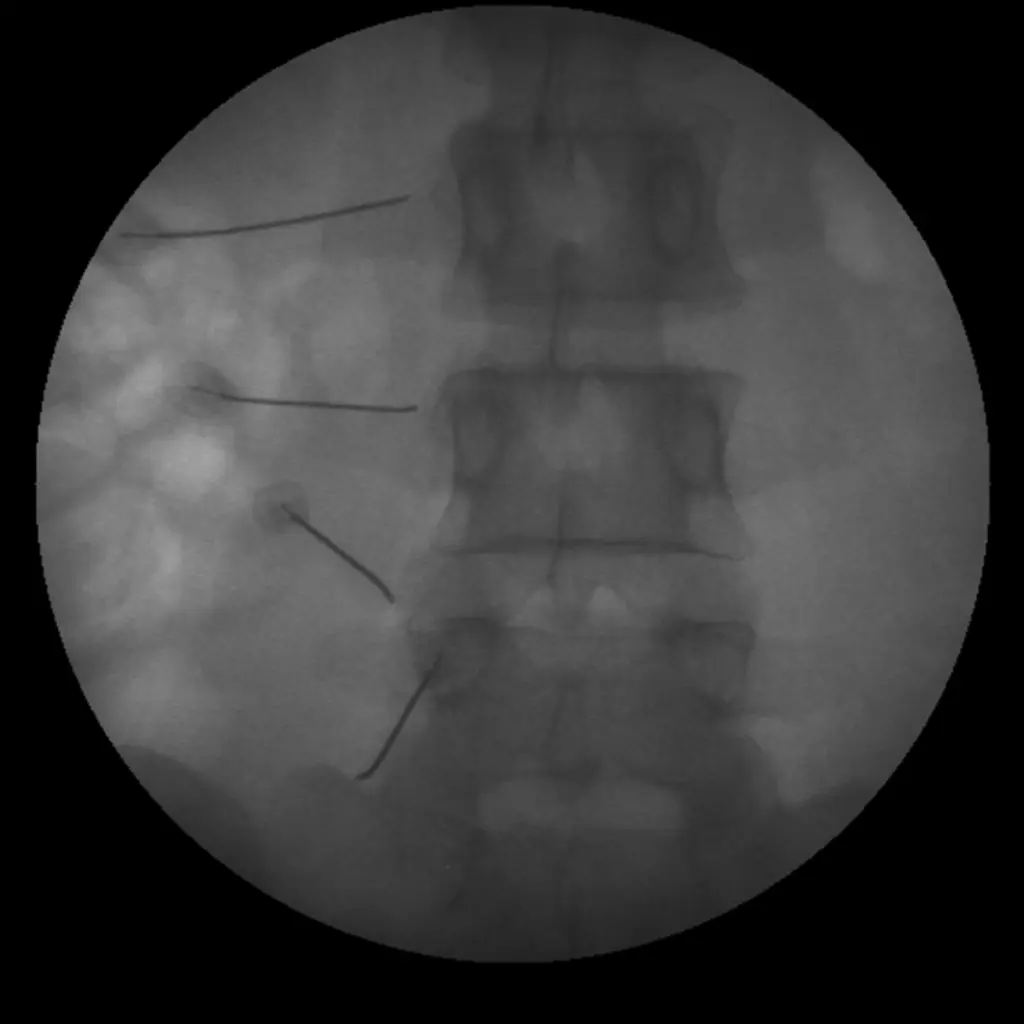
Lumber spine facet joint RF ablation procedure – AP view
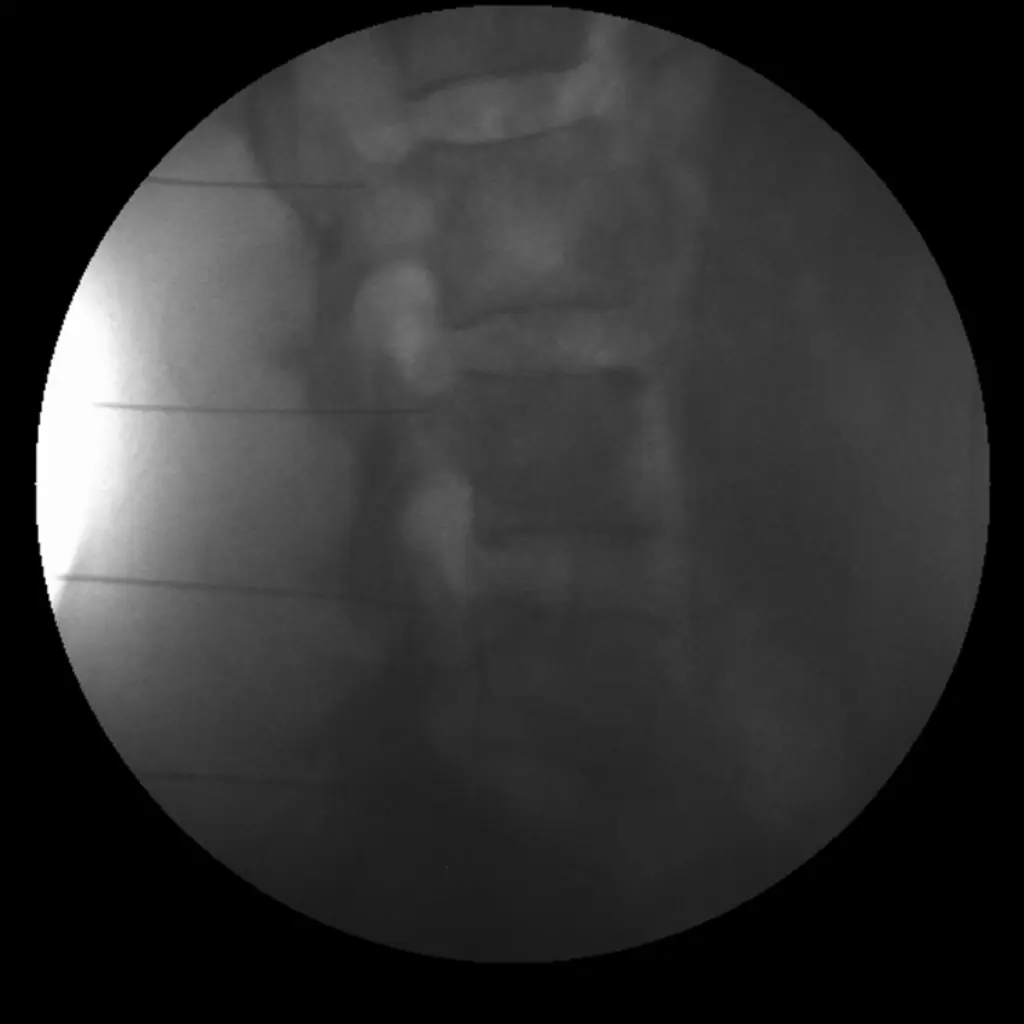
Lumber spine facet joint RF ablation procedure – Lateral View
Application In Following Condition
We are using Radiofrequency ablation technology for Low back pain, cervical pain, neuropathic pain and cancer-related pain management. Following are the common examples in which we are doing treatment with RF ablation,
- Lumber / Cervical Spine Facet Joint Pain (Medial branch RF)
- Degenerative Disc Disease (Intradiscal RF Biaculoplasty)
- Cancer related radicular pain (DRG Pulse RF)
- Sacro Iliac Joint Pain (Pulse RF Neuromodulation)
- Vertebral body metastasis in cancer pain (Remi communicant RF)
- Trigeminal neuralgia (Gassarian ganglion RF)
- Atypical Facial Pain (Sphenopalatine ganglion RF)
- Upper limb CRPS Type I & II (Stellate ganglion RF)
- Lung / Pulmonary metastasis (T2-T3 ganglion RF)
- Abdominal malignancy (Splanchnic ganglion RF)
- Ischemic Lower limb pain (Lumber sympathetic plexus RF)
- Pelvic organ malignancy (Superior hypogastric plexus RF)
- Genital organ malignancy, Atypical vaginal pain (Ganglion Impar RF)
- Post Herpetic Neuralgia (Intercostal nerve Pulse RF)
- Shoulder pain (Suprascapular nerve Pulse RF)
- Post Hernia Surgery pain (Ilioinguinal / Genitofemoral nerve Pulse RF)
- Knee arthritis (Genicular nerve RF)
- Neuropathic pain
- CRPS Type I & II
- Cancer related pain