Shoulder Specialist in Ahmedabad
Frozen Shoulder
Frozen shoulder is a misnomer. Actually, its meaning is not able to move the shoulder joint freely and properly. We have to diagnosed the shoulder pain inside the shoulder joint and doing treatment according to the reason find in shoulder joint.
Problem inside the shoulder joint starting from joint to skin
- The shoulder is the most movable joint in the body. However, it is an unstable joint because of the range of motion allowed. It is easily subject to injury because the ball of the upper arm is larger than the shoulder socket that holds it. To remain stable, the shoulder must be anchored by its muscles, tendons, and ligaments.
- Some shoulder pain arises from the disruption of these soft tissues as a result of injury or from overuse or underuse of the shoulder.
- Other problems arise from a degenerative process in which tissues break down and no longer function well.
- Shoulder pain may be localized or may be referred to areas around the shoulder or down the arm.
- Disease within the body (such as gallbladder, liver, or heart disease, or disease of the cervical spine of the neck) also may generate pain that travels along nerves to the shoulder.
- Pain around the shoulder is one of the common problems particularly in elderly patients. Degenerative diseases and overuses are common in shoulder along with inflammatory conditions.
How to confirm the diagnosis
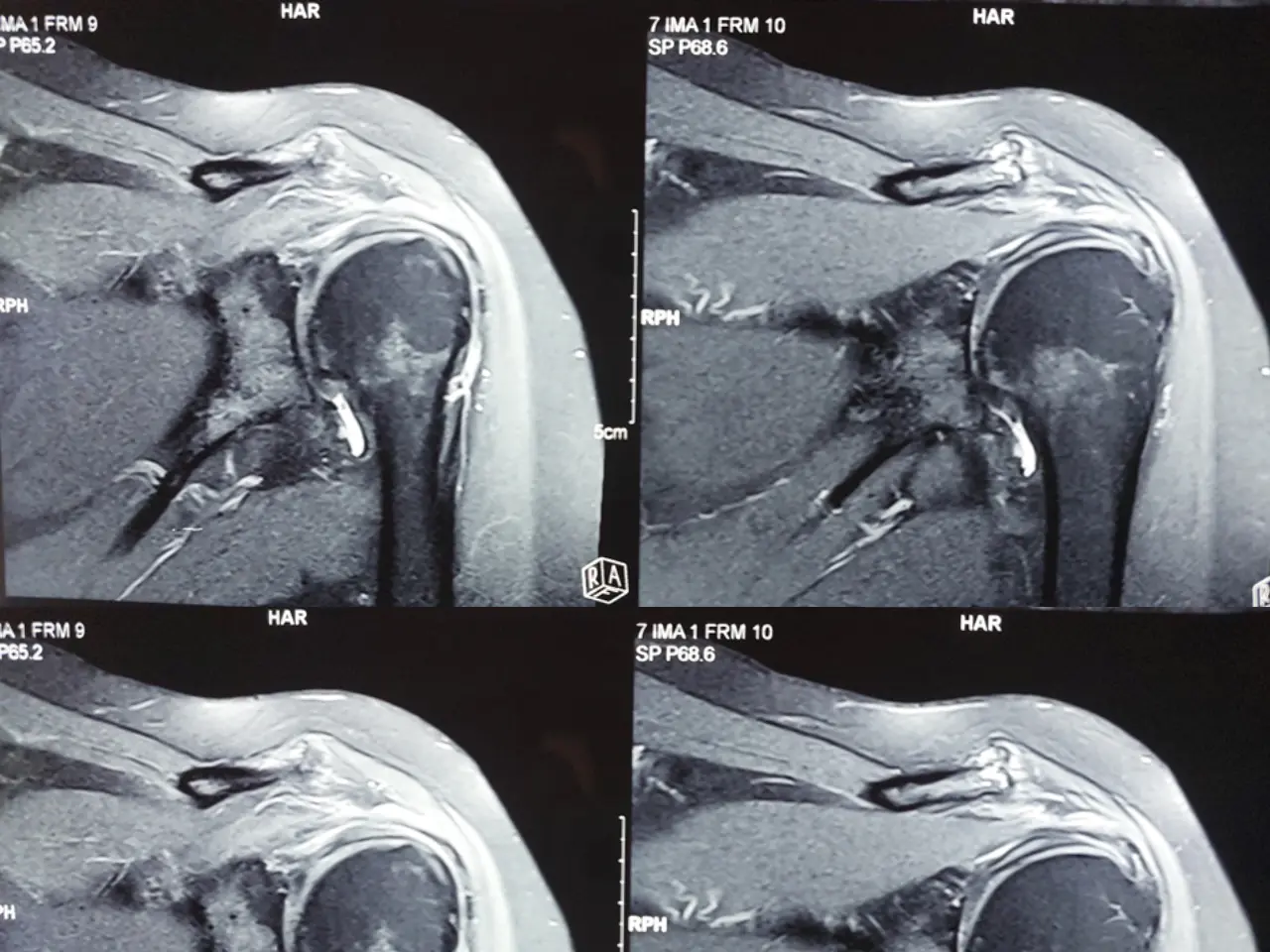
- Shoulder pain patient should check clinically with detail history and examination of patient by our pain physician doctor.
- After proper evaluation of patient if required we can do x-ray, ultrasonography (USG) or MRI.
- MRI is a gold standard investigation for diagnosis of shoulder pain. We can perfectly diagnosis the all problem related to shoulder in that.
Common causes
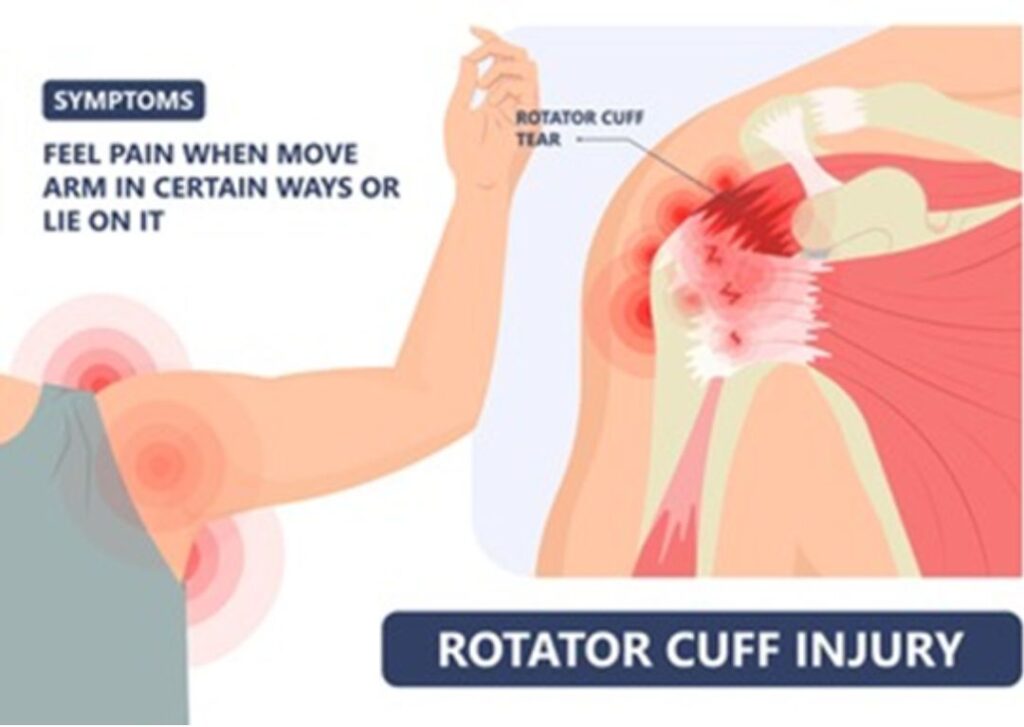
Rotator Cuff Injuries
Rotator cuff are made of four muscle which are helpful to the whole ” Range Of Movement ” of shoulder joint. This muscles are Supraspinetus , Infraspinetus, Teres major & Subscapularis. Among the all muscle the most commonly affected muscle is “Supraspinetus”. This muscle is very much prone to injuries as it comes behind the shoulder and passes tunnel below the acromian process and attached to the grater tuberocity of humerus. Inflammation of tendon represented as Tendinitis, Tendinosis. Injuries of tendon represented as partial or complete tear of tendon. Patient presented with painful movement of shoulder and sometime restriction of movement with ‘painful arc’ in abduction of arm.
Subacromial Bursitis
This is another common cause of shoulder pain. Inflammation of a pouch of synovial fluid which is located in the shoulder. It is most often caused by some sort of trauma or overuse of the shoulder. It is difficult to distinguish between subacromial bursitis and rotator cuff injury.

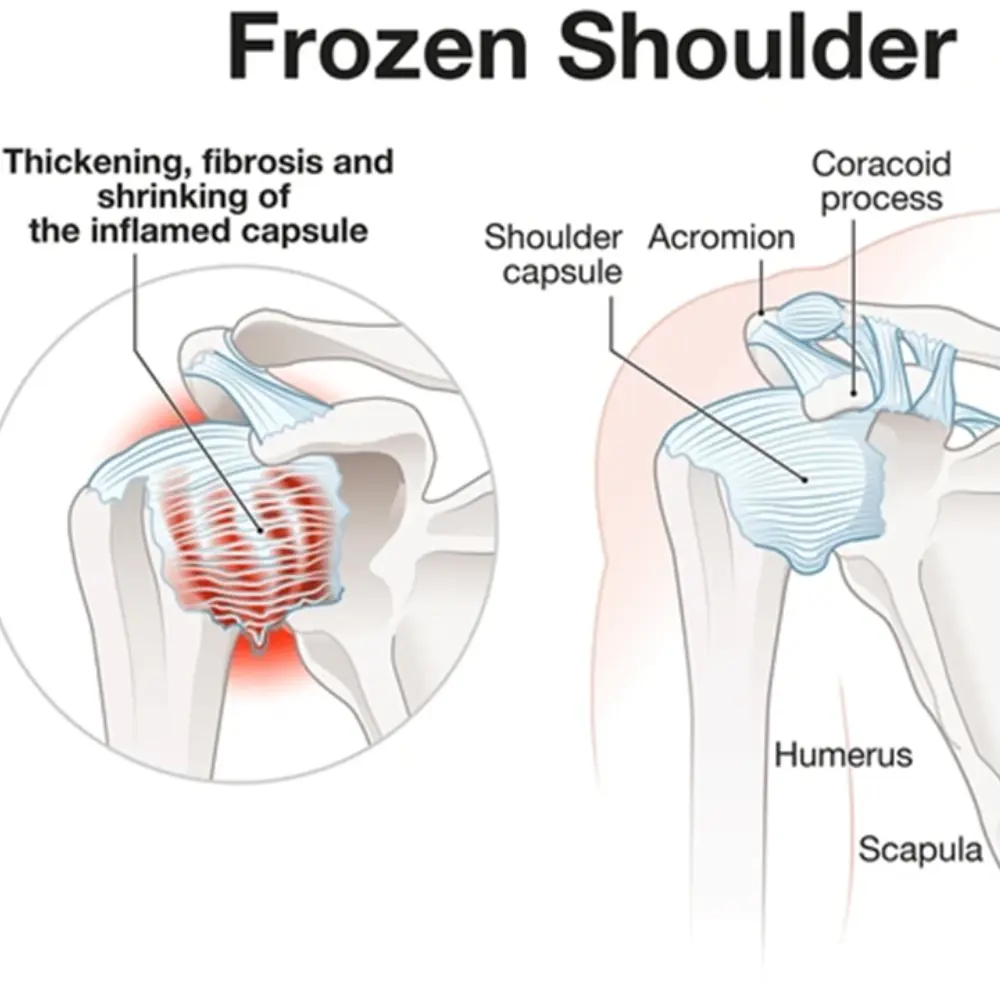
Adhesive Capsulitis
Capsule of shoulder joint is to protect the joint. But many condition causes the inflammation of capsule and make it thick and sticky which causes the capsule to become adhesive to the joint and restriction of joint movement develop gradually causes shoulder pain Common causes of “Adhesive Capsulitis” are:
- Diabetes mallitus
- Thyroid problems
- Post traumatic / Post Immobilization
- Post shoulder surgery
- Connective tissue disease
Calcific Tendinitis
Long term inflammation along the tendon of rotator cuff causes gradual deposition of calcium along the tendon sheath and causes the painful movement of tendon inside the sheath. Clinically patient presented with shoulder pain on abduction and forward flexion.
Shoulder Joint Osteo-Arthritis
Osteo-arthritis of shoulder joint is also common problem. Common causes are age related arthritis, Rheumatoid arthritis, post infective arthritis, Post traumatic arthritis & collagen vascular disease. Clinically patient presented with reduce range of movement with pain in both active and passive motion of shoulder.
Management of shoulder pain
Once final diagnosis is confirmed by history, clinical examination & investigation shoulder pain might be managed by different modalities of treatment.
Conservative management
- In conservative management we can give treatment in form of Analgesics, Physiotherapy & exercise. Many times, mild pain of shoulder will be resolve with this treatment.
- After 2 to 3 weeks of conservative treatment if shoulder pain is not resolves then we should go for advance treatment according to pathology of shoulder.

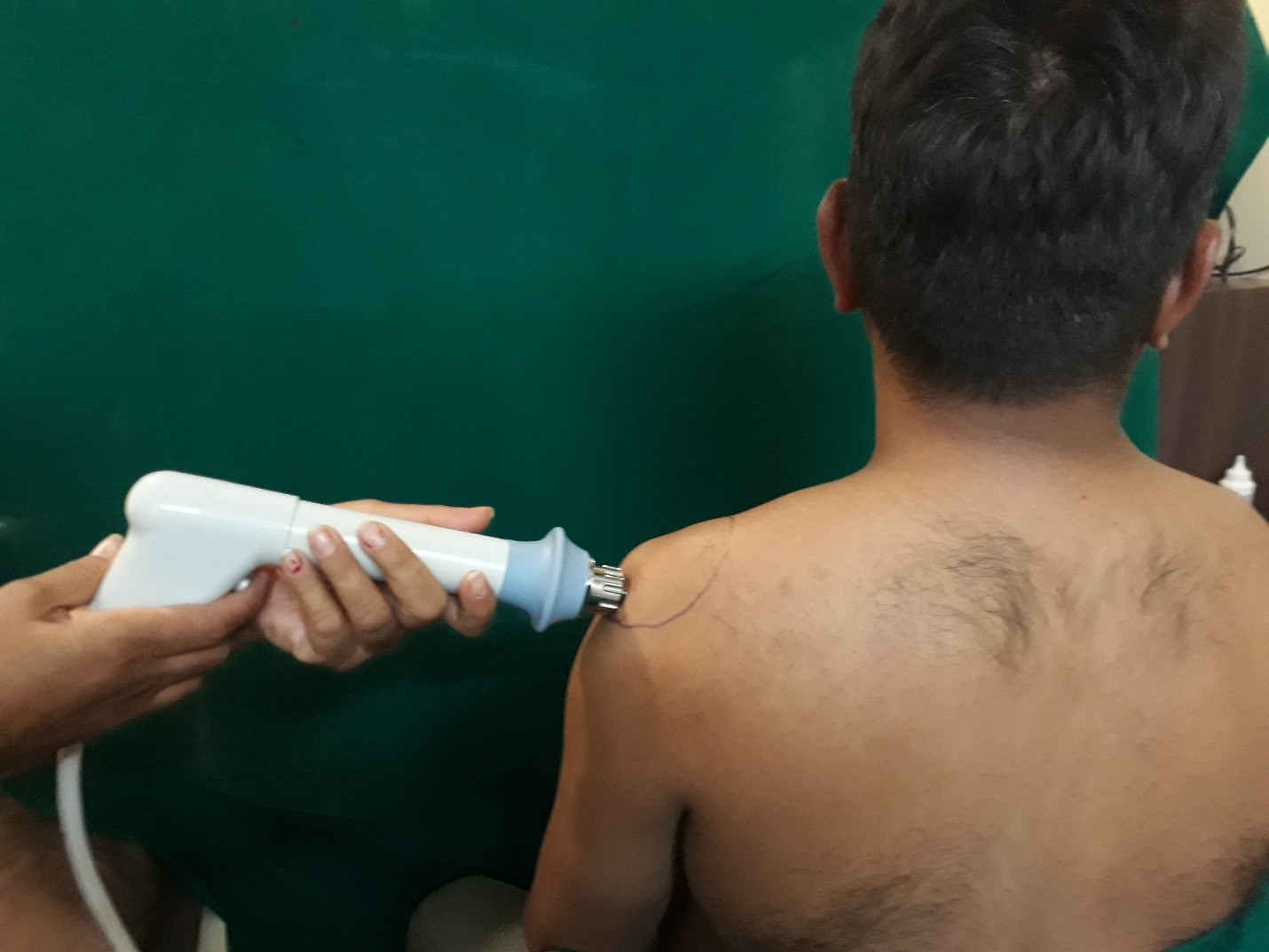
- High intensity laser & Extra corporeal shock wave lithotripsy are the two powerful machine which was imported from U.K.
Indication: Supraspinatus tendinitis, Bicipital tendinitis, Rotator cuff partial tear, Ligament pain, Muscular pain, Acromioclavicular joint pain, Subacromial bursitis
Mode of Action: High-intensity laser is a 12 w machine which is 100 times more powerful than ordinary Ultrasound or Low-level laser therapy machine. Laser light will be absorbed in mitochondria of cells, it regenerates the ATP in the cell and replace the degenerative tissue. Laser light also increase the vascularity of the affected tissue to washout the toxin from it. Laser had two mode of treatment analgesia & bio stimulation.
It is same but more powerful machine which is used for musculotendinous pain management. Shock wave produce beneficial effects including Neovascularization ingrowth, reversal of chronic inflammation, stimulation of collagen and dissolution of calcium build-up. Stimulation of this biological mechanisms creates an optimal healing environment. As the injured area is returned to normal, functionally is restored and pain is relieved.
PRP Treatment
Rotator cuff partial tear, Supraspinatus tendon partial injury, Early arthritis of shoulder joint, Acromioclavicular joint arthritis, Subacromial bursitis.
PRP is high concentration of platelets which has 4 to 5 times more than blood. Platelets have various growth factors causes the healing of injured tissue. We can inject PRP in injured tissue with use of ultrasonography (USG) so that it reaches in maximum concentration in tissue. For arthritis of shoulder joint (early grade 1 & 2) we can give PRP therapy repeatedly once a month for 4 to 5 months. For Rotator cuff or Supraspinatus partial tear we can inject intrasubstance in muscle or tendon one to two times. Effect of PRP is gradual onset and it take one or two months for complete effect.